让微服务支持分布式事务
约 744 字大约 2 分钟
2025-02-12
要支持分布式事务,数据库对象必须实现 IStorageEngine 接口。
以 Sqlite 数据库为例
打开你的微服务工程,把 SystemDBContext.cs 改造成下面的样子,并确保它的依赖注入方式为 AddScoped:
public class SystemDBContext : IDisposable , IStorageEngine
{
SqliteConnection _connection;
public SystemDBContext()
{
_connection = new Microsoft.Data.Sqlite.SqliteConnection("data source=./data.db");
_connection.Open();
}
public SqliteConnection Connection => _connection;
/// <summary>
/// 当前事务对象
/// </summary>
public object CurrentTransaction { get; set; }
SqliteTransaction _transaction;
public void BeginTransaction()
{
if(CurrentTransaction == null)
this.CurrentTransaction = _transaction = _connection.BeginTransaction();
}
public void CommitTransaction()
{
_transaction?.Commit();
this.CurrentTransaction = null;
}
public void RollbackTransaction()
{
_transaction?.Rollback();
this.CurrentTransaction = null;
}
public void Dispose()
{
_transaction?.Dispose();
this.CurrentTransaction = _transaction = null;
_connection.Dispose();
}
}让 Controller 的方法支持分布式事务
public class DemoController : BaseController
{
/// <summary>
/// 我的第一个接口
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name">姓名</param>
/// <param name="age">年龄</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public string HelloWorld(string name,int age)
{
return $"Hi,{name} - {age}";
}
/// <summary>
/// 我的第一个支持分布式事务的方法
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public async Task CreateYourTable()
{
//开启分布式事务
this.CurrentDBContext.BeginTransaction();
//编写业务逻辑
using var cmd = this.CurrentDBContext.Connection.CreateCommand();
cmd.Transaction = this.CurrentDBContext.CurrentTransaction;
cmd.CommandText = @"
CREATE TABLE if not exists ""userinfo"" (
""id"" INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
""username"" VARCHAR(50) COLLATE NOCASE
);
";
await cmd.ExecuteNonQueryAsync();
//不要提交事务,否则无法支持分布式事务
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 添加用户
/// </summary>
/// <param name="userName"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public async Task AddUser(string userName)
{
//开启分布式事务
this.CurrentDBContext.BeginTransaction();
//编写业务逻辑
using var cmd = this.CurrentDBContext.Connection.CreateCommand();
cmd.Transaction = this.CurrentDBContext.CurrentTransaction;
cmd.CommandText = "insert into userinfo (username) values (@p0)";
var param = cmd.CreateParameter();
param.ParameterName = "@p0";
param.Value = userName;
cmd.Parameters.Add(param);
await cmd.ExecuteNonQueryAsync();
//不要提交事务,否则无法支持分布式事务
}注意
上面代码中,是没有提交事务的,因为事务提交是由底层框架控制,你只需要启动事务就可以了。
也就说,只要你的方法体有 this.CurrentDBContext.BeginTransaction(),并且后面没有主动提交或者回滚事务,那么这个方法就是支持分布式事务的。
建议大家在编写 controller 接口时,只要涉及到数据变动,都应该习惯性地让它支持分布式事务。
以 Entity Framework 为例
如果你是使用 Entity Framework,那么把 SystemDBContext.cs 文件删除,然后把 SystemDBContext.EF.cs 里面的注释取消,接着把 SystemDBContext 的父类改为你的 DbContext 类即可。
同样需要确保 SystemDBContext 的依赖注入方式为 AddScoped
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddDbContext<SystemDBContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection")),
ServiceLifetime.Scoped);
}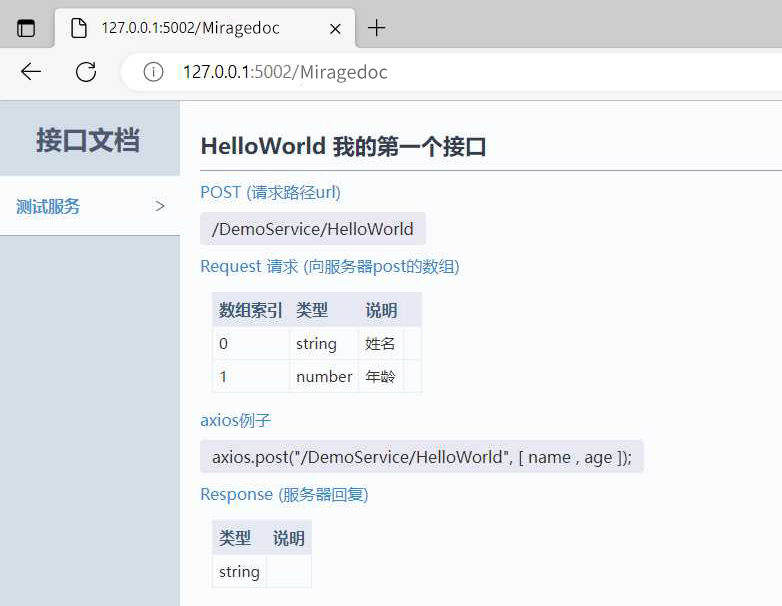
从文档描述来看,通过 post json 的方式,把参数组合成数组,提交到 WebApi 即可。 简单写个 js 代码测试一下:
<script>
async function test(name,age) {
var ret = await fetch("http://127.0.0.1:5002/DemoService/HelloWorld",
{
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify([name, age])
});
if (ret.status == 200) {
alert(await ret.text());
}
else
alert("error");
}
test("Jack", 666);
</script>接口分类
如果一个 Controller 里面有较多的方法,那么,可以使用 CategoryAttribute 对方法进行分类显示。
/// <summary>
/// 获取系统详情
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
[Category("详情")]
public Task<Info[]> GetInfos()
{
...
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取账户详情
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
[Category("详情")]
public Task<Account> GetAccountInfo()
{
...
}呈现的效果如下:

